https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abstract_syntax_tree
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parse_tree
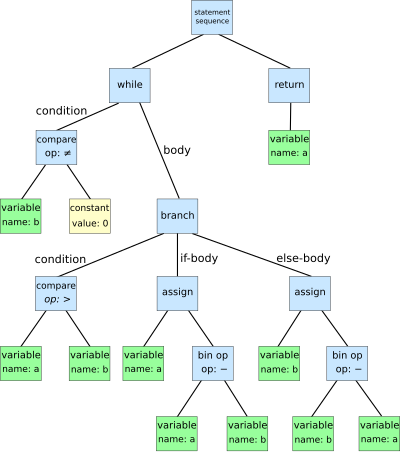
citation:
Left Hand Side vs. Right Hand Side
For example, in a = b + c, we evaluate the value of b and c, add them together, and then associate or store the result in a. Here b and c have the context that we call right hand side — b and c are on the right hand side (of an assignment), whereas a has left hand side context — a is on the left hand side of an assignment. We need the value of b and c yet the location of a to store the result.
A complex left hand side expression will itself also involve some right hand side evaluation. For example, a[i] = 5 requires evaluting a and i as values (as if right hand side) and only the array indexing itself is evalutated as left hand side (for storage location). 5, of course, is understood as right hand side.
Leave a Reply